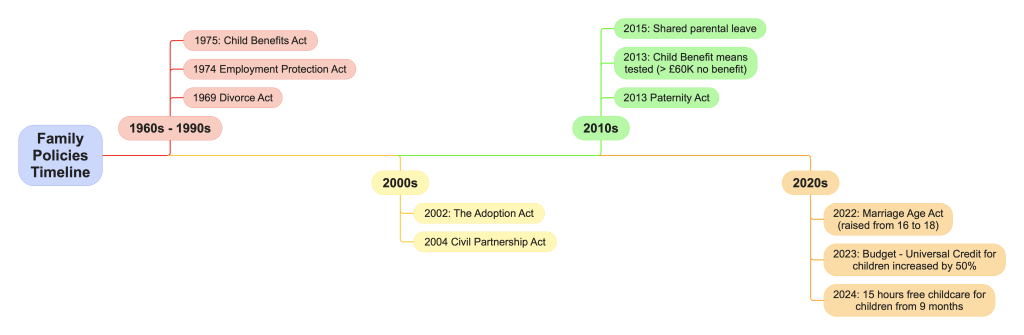
This post defines social policy and then examines the 1969 Divorce Act, Maternity and Paternity Acts, the Civil Partnership Act and Child Benefit policies, looking at how these policies have impacted different aspects of family life such as marriage, divorce, family structure, as well as the differential impact on men, women and children within the family.
Social policy refers to the plans and actions of state agencies such as health and social services, the welfare benefits system and schools and other bodies.
Policies are usually based on laws introduced by governments that provide the framework within which these agencies will operate. For example, laws lay down who is entitled to each specific welfare benefit.
Most social policies affect families in some way or other. Some are aimed directly at families, such as laws governing marriage and divorce, abortion or contraception, child protection, adoption and so on.
Policies are not necessarily aimed specifically at families but will have an effect in families. Such policies would include those on childcare, education, housing, and crime. Furthermore, many policies that impact upon families are those that make changes to the legislation on taxation and benefits, such as child tax credits.
Recently, the Department for Education and Skills has been given a new name and expanded role. The creation of the Department for Children, Schools and Families suggest that the current government believe that to make a better society for the children of today, family life and education should not be treated as two separate areas of life.
There are many social policies which have affected family life over the years, so the summary below is necessarily selective!

The most well-known act is probably the 1969 Divorce Act which made getting a divorce MUCH easier. Since then, the main policies have been focused on equalising marriage for same-sex couples and most recently raising the legal age of marriage from 16 to 18.
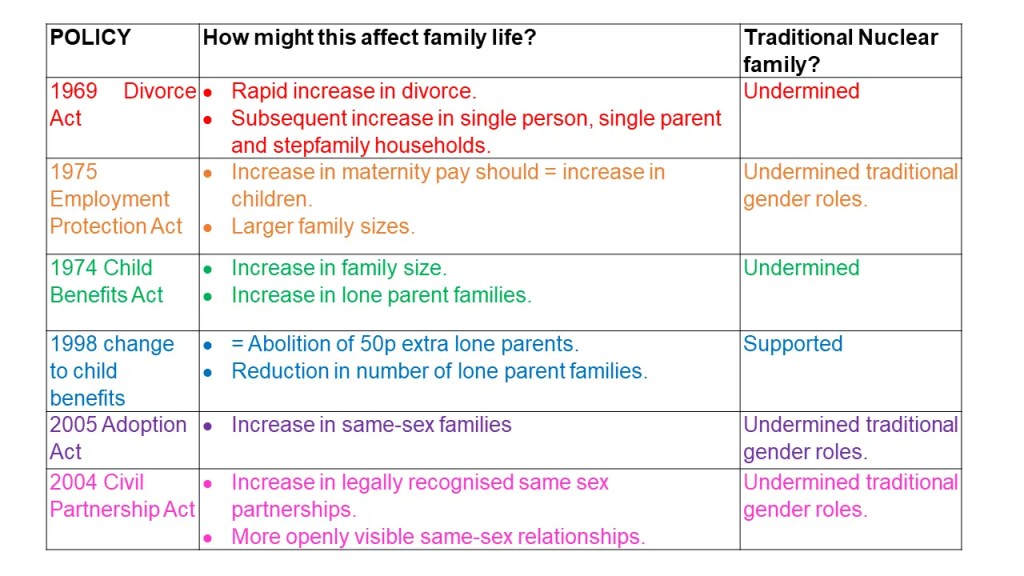
Before 1969, one partner had to prove that the other was ‘at fault’ to be granted a divorce, however, following the Divorce Reform Act of 1969, a marriage could be ended if it had irretrievably broken down, and neither partner no longer had to prove “fault”. However, if only one partner wanted a divorce, they still had to wait 5 years from the date of marriage to get one. In 1984 this was changed so that a divorce could be granted within one year of marriage.
The Civil Partnership Act 2004 gave same-sex couples the rights and responsibilities like those in a civil marriage. The Act was introduced by the New Labour government in power at the time. Civil partners are entitled to the same property rights, the same exemptions on inheritance tax, social security, and pension benefits as married couples. They also have the same ability to get parental responsibility for a partner’s children as well as reasonable maintenance, tenancy rights, insurance, and next-of-kin rights in hospital and with doctors. There is a process like divorce for dissolving a civil partnership.
There were 60 938 Same-Sex Civil Partnerships formed between 2004 and 2013, with annual numbers being around 6500 a year following an initial spike in the first couple years. From 2013 annual numbers of same-sex civil partnerships dropped to fewer than 1000 a year reflecting the fact that from 2013 same-sex couples were allowed to get married on the same basis as opposite-sex couples.

Since 2019 opposite-sex couples can also enter civil-partnerships and in 2021 6000 couples did so, but these numbers may be lower because of Covid-19 restrictions on social gatherings.
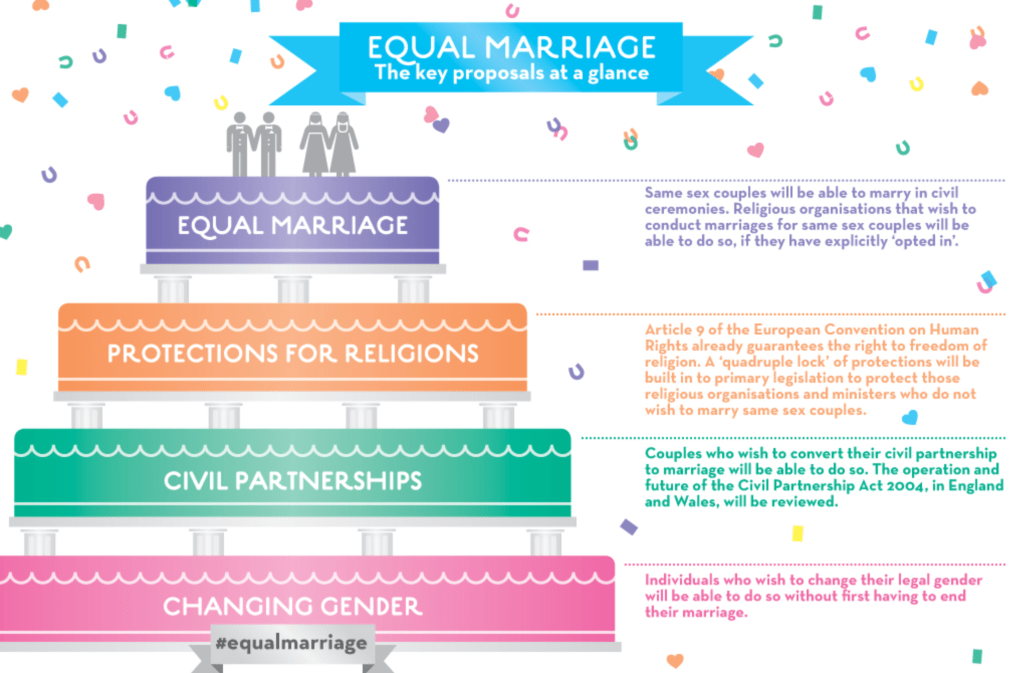
This act allows same-sex couples to enter a marriage in England and Wales on the same basis as opposite-sex couples, and to convert Civil Partnerships to Marriages. Statistics from the ONS suggest that same-sex couples prefer marriage over civil partnerships as there were approximately 6000 same-sex marriages in 2019, which reflects the drop off in the number of civil partnerships since marriage has been an option.
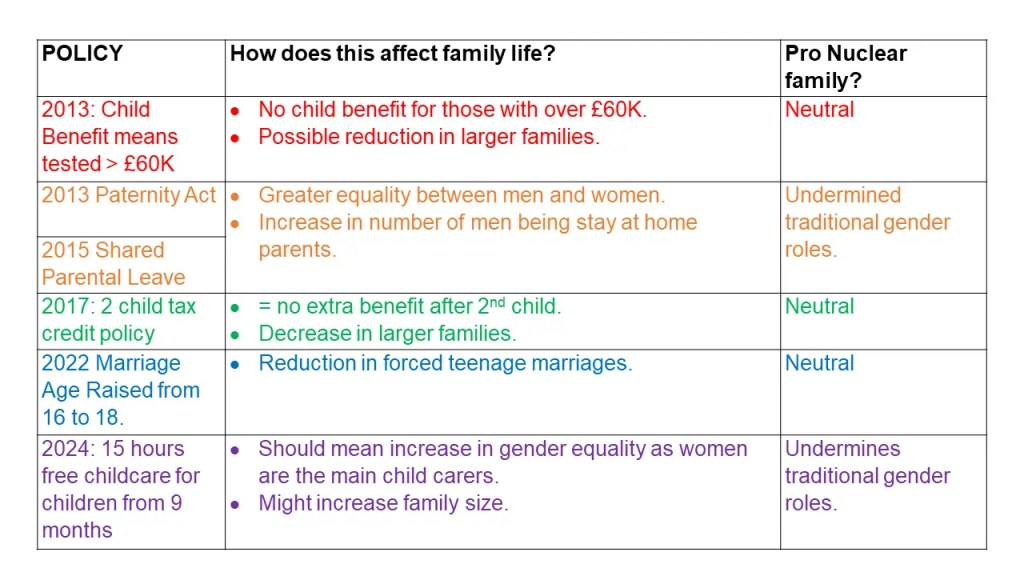
In 2022 the minimum age of marriage in England and Wales was raised to 18. Previously it had been possible for 16 and 17 year olds to get married with parental consent. Since 2022 it is illegal to force children, including 16 and 17 year olds to marry and to do so could incur a jail sentence of up to seven years in prison. The act also covers more ‘informal’ non-legally binding ceremonies.

Fathers are only entitled to up to two weeks of paternity leave, paid at the same rate as the final 33 weeks of maternity leave pay for mothers (£172.48 per week or 90% of weekly average earnings, whichever is lower.
Since 2015 parents can apply for up to 50 weeks of Shared Parental Leave, up to 37 weeks of which are paid. For this to work the woman must swap her maternity leave for shared leave, this isn’t extra leave for the father.
There is quite a long history of changes to maternity and paternity policy….
Social responsibility for women’s health during childbearing was first recognised through the 1911 National Insurance Act. It included a universal maternal health benefit and a one off maternity grant of 30 shillings for insured women (around £119 in today’s money)
However, many women were routinely sacked for becoming pregnant until the late 1970s and the UK only introduced its first maternity leave legislation through the Employment Protection Act 1975. However, for the first 18 years (until 1993!) only about half of working women were eligible for it because of long qualifying periods of employment. The act was amended in 1993 so that all pregnant women got a minimum of 14 weeks statutory maternity leave regardless of prior employment
In 2003, male employees received paid statutory paternity leave for the first time, an entitlement that was extended in January 2010.
Since 2010 (following what is often called the ‘Paternity Act’) – This leave is divided into two 26-week periods. After the first 26 weeks, the father of the child (or the mother’s partner) has the right to take up to 26 weeks’ leave if their partner returns to work, in effect taking the place of the mother at home. It is unlawful to dismiss (or single out for redundancy) a pregnant employee for reasons connected with her pregnancy.
From 2015, parents will be given the right to share the care of their child in the first year after birth. Women in employment will retain their right to 52 weeks of maternity leave. Only mothers will be allowed to take leave in the first two weeks’ leave after birth. But after that parents can divide up the rest of the maternity leave.
Child benefit is payable for every child parents have, although if you’re a parent who earns more than £60 000 in 2023 you have to pay back all of it in the form of extra taxes.
Child Benefit has been around for almost 50 years!
The Child Benefit Bill introduced for the first time a universal payment, paid for each child. The rate payable was £1/week for the first and £1.50 for each subsequent child. An additional 50p was payable to lone-parent families.
Child Benefits increased in line with inflation, until 1998, when the new Labour government increased the first child rate by more than 20% and abolished the Lone Parent rate. Rates increased again in line with inflation until 2010, since which time they have been frozen.
Effective from 7 January 2013, Child Benefit became means tested – those earning more than £50,000 per year would have part of their benefit withdrawn, and if earning over £60,000, would receive nothing at all.
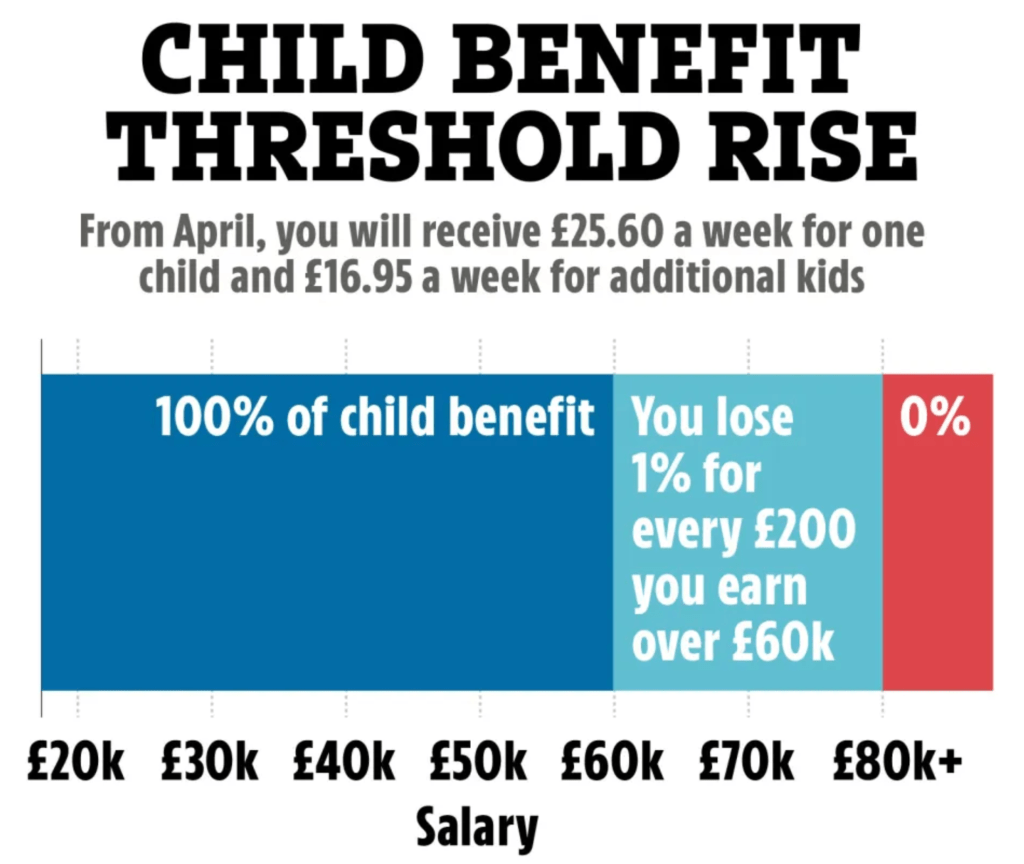
In 2024 everyone with children receives child benefit payments in the following amounts:
These payments are awarded for children up to the age 16 and up to age of 20 if they stay on in further or higher education.
They are payable to everyone whether working or in receipt of Universal Credit and the payments are in addition to the child payment part of universal credit.
However, for those earning £50 000 or more a year, they pay additional taxes: a ‘child tax credit charge’ which recoups some of the money received in child benefit, and for those earning £60K a year, they pay so much this cancels out the entire amount they will receive in child benefit.
Universal Credit was introduced in 2013 to replace a wide range of other individual benefits including income support, housing benefit, working tax credit and child tax credit.
The total amount of universal credit for single people is just under £15 000 a year and for a single person or couple with children the cap is £22 000 a year (if they have two children living with them).
The general idea behind universal credit is to encourage people into work by making sure they are not earning less when working in part-time or low-paid jobs compared to claiming benefits. Prior to Universal Credit the benefits system had perverse incentives meaning you could earn less working 16 hours a week than on benefits because when you started working more than 16 hours per week JobSeeker’s Allowance would stop and you would lose your housing benefit. Under Universal Credit this doesn’t happen because if your earnings are below £15000 (if you’re a single person), they are ‘topped up’, thus encouraging more people into work (3)
In 2023, people with children who are eligible for Universal Credit receive £315 for their first child and then £270 for their second child, payable until those children turn 18 (assuming they stay in education) and then no further payments for any further children they have after the first two (unless they already had three or more children before 2017 and were already claiming the previous child tax credit and transferred onto Universal Credit).
The money paid by the government for children (the ‘child tax credit’ part of universal credit, if you like) is part of that overall cap. If someone’s overall Universal Credit amount is greater than £22 000 when they start receiving more money because of having two children, universal credit would automatically adjust downwards to the upper cap.
In 2005, under New Labour, the law on adoption changed, giving unmarried couples, including gay couples, the right to adopt on the same basis as married couples.
This topic is part of the families and households module, normally taught in the first year of A-level sociology.
You might also like this brief video on… How do Social Policies Affect Family Life?
(3) This is a simplified version, things are a little more complex, to see more: Gov.UK (Accessed May 2023) Universal Credit Allowances